The Building Phylogenetic Tree dialog for the MrBayes method has the following view:
There are two steps to a phylogenetic analysis using MrBayes:
- Set the evolutionary model.
- Run the Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) analisys.
The evolutionary model is defined by the following parameters:
Substitution model — specifies the general structure of a DNA substitution model. This parameter is available for the nucleotide sequences. It corresponds to the Nst setting of MrBayes. You may select one of the following:
- JC69 (Nst=1)
- HKY85 (Nst=2)
- GTR (Nst=6)
Rate matrix (fixed) — specifies the fixed-rate amino-acid model. This parameter is available for amino-acid sequences. The following models are available:
- poisson
- jones
- dayhoff
- mtrev
- mtmam
- wag
- rtrev
- cprev
- vt
- blosum
- equaline
The following parameters are common for nucleotide and amino-acid sequences:
Rate — sets the model for among-site rate variation. Select one of the following:
- equal — no rate variation across sites.
- gamma — gamma-distributed rates across sites. The rate at a site is drawn from a gamma distribution. The gamma distribution has a single parameter that describes how much rates vary.
- propinv — a proportion of the sites are invariable.
- invgamma — a proportion of the sites are invariable while the rate for the remaining sites are drawn from a gamma distribution.
Gamma — sets the number of rate categories for the gamma distribution.
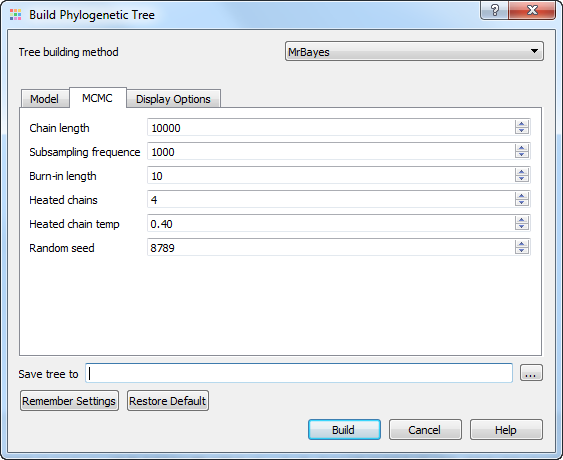
You can select the following parameters for the MCMC analisys:
Chain length — sets the number of cycles for the MCMC algorithm. This should be a big number as you want the chain to first reach stationarity, and then remain there for enough time to take lots of samples.
Subsampling frequency — specifies how often the Markov chain is sampled. You can sample the chain every cycle, but this results in very large output files.
Burn-in length — determines the number of samples that will be discarded when convergence diagnostics are calculated.
Heated chains — number of chains will be used in Metropolis coupling. Set 1 to use usual MCMC analysis.
Heated chain temp — the temperature parameter for heating the chains. The higher the temperature, the more likely the heated chains are to move between isolated peaks in the posterior distribution.
Random seed — a seed for the random number generator.
Display tree in new window - displays tree in new window.
Display tree with alignment editor - displays tree with alignment editor.
Synchronize alignment with tree - synchronize alignment and tree.
Save tree to — file to save the built tree.
Press the Build button to run the analysis with the parameters selected and build a consensus tree.