The 'mfold' software is a tool for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. It was developed by M. Zuker in the late 1980s for RNA folding and improved for DNA folding in 1996. mfold uses nearest neighbor energy rules.
Tool home page: mfold.org. Similar results to those produced by UGENE can be obtained using the mfold web server (DNA prediction, RNA prediction) or using the OligoAnalyzer tool. For complete documentation on the tool, see a) on the website, b) in the article, c) in the source code in the corresponding folder.
UGENE uses Ghostscript to convert PS files to PNG and PDF.
ToC
Open the dialog
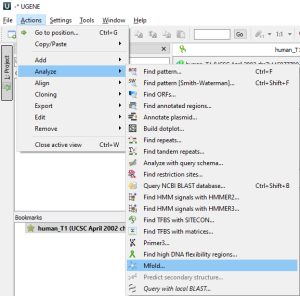
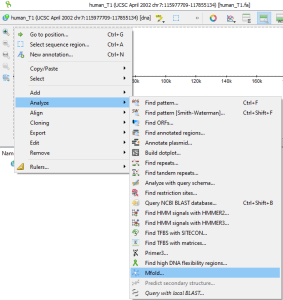
mfold only works with DNA or RNA sequences. You can trigger the dialog from
by selecting the appropriate Sequence View Global action
or through the Main Menu→Actions→Analyze
or through the Sequence Context Menu→Analyze
This is what the mfold dialog looks like
Input parameters
The tool is passed explicit and implicit parameters. Explicit parameters are set in the dialog, implicit parameters are taken from the sequence context.
Algorithm settings
For complete settings details, see the documentation on the mfold website or documentation in source.
This is the Settings section of the mfold settings tab.
| Parameter | Unit | Default | Limits | Tool argument name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | °C | 37 | [0,100] | T | The folding temperature. For RNA this is always the default value. For DNA it is taken from the dialog. |
| Ionic conditions | M | Na=1 | [0,1.5] | NA_CONC | Ionic conditions are used to enter total monovalent (Na) and divalent (Mg) ions concentrations. For RNA this is always the default values. For DNA it is taken from the dialog. |
| Mg=0 | MG_CONC | ||||
| Percent suboptimality | % | 5 | [1,100] | P | The suboptimality percentage controls the free energy increment δδG for computing suboptimal foldings. Only foldings with a free energy ≤ΔG+ δδG will be computed, where ΔG is the predicted minimum free energy. Normally, δδG=P/100|ΔG|, but it is rounded up to 1 kcal/mol or down to 12 kcal/mol if it is outside this range. |
Tool comparison